Read Time: 13 Minutes
Morningstar Ratings
At its current rate, the managed investment vehicles universe will surpass one million products in three years. Morningstar’s rating system cuts through the complexity.
Ratings help investors understand how investments work, if they’re worthwhile, and their role in a portfolio. Asset and wealth managers can prune the ever-growing list of investment options to create one innovative product or personalized portfolio.
More than just managed products, Morningstar covers the full investing landscape—economic moats, managers, ESG factors, and more—with meticulous, time-tested methods.
Key Takeaways
- Morningstar’s team of independent manager researchers is one of the largest in the world.
- The rating system covers over 600,000 investment products globally.
- Ratings are a reliable first step in the investment evaluation process.
Morningstar Ratings Explained
Morningstar ratings are an initial tool to screen, sort, and analyze opportunities. Ratings help you make confident investment decisions powered by research on the fundamentals.
Morningstar debuted with its mutual fund ratings, the first of its kind. Today, our data extends to over 600,000 investment vehicles. And our coverage is always growing.
Are Morningstar ratings reliable? Should I trust their ratings?
Morningstar has conducted independent investment research since 1984. Our analysts have the freedom to ask tough questions and challenge popular opinion.
Morningstar regularly conducts reviews to understand how well ratings work.
Why choose Morningstar for rating investments?
Morningstar ratings give you one instantly understandable indicator of an investment’s potential. From there, you can dig into detailed analysis.
Financial advisors can use ratings to clearly explain a proposal. Answer questions like: Where is my money invested? How am I protected from market downturns? How will this portfolio help me reach my goals?
Asset managers can compare investments and validate investment ideas. As a common language, ratings in marketing materials showcase a fund’s strengths.
Where can I find Morningstar ratings?
Wealth and asset managers can augment their research with ratings and in-depth analysis in professional Morningstar software. Investors can find our ratings for free on morningstar.com by searching the stock ticker symbol.
What is the best Morningstar rating?
Morningstar ratings don’t endorse any securities. Almost all of our ratings compare investments against others in the same category, and do not indicate an absolute best or worst.
Instead, our research and data help investors understand their options from multiple angles. Pair ratings with in-depth analyst commentary and supporting data to fully evaluate an investment.
How often do Morningstar ratings change?
Most Morningstar ratings update monthly. Morningstar Medalist Ratings derived by our analysts are re-evaluated each year. Quantitatively-derived Medalist Ratings can update more often while upholding the same level of analyst input.
How are Morningstar ratings calculated?
Morningstar’s global research team follows the same methods to ensure that investments are held to the same standards of integrity. Ratings combine the best of machine learning and human insight.
Find Ratings in Our Products and Services

Direct Web Services
.png?auto=webp&disable=upscale&width=100)
Morningstar Data

Morningstar Direct℠

Morningstar Research
Key Takeaways

The Morningstar Rating for stocks can help investors uncover undervalued stocks.

The fair value estimate is an analyst’s perspective on the long-term intrinsic value of a stock.

The Morningstar Economic Moat Rating measures a firm’s sustainable competitive advantage.
Morningstar Ratings For Stocks
Introduced in 2001, the Morningstar Rating for stocks can help investors discover stocks that are truly undervalued. Our research covers 51,000 public companies. Ratings update daily.
Our analysts calculate the star rating range by reviewing:
- A stock’s current price.
- The fair value estimate and uncertainty level.
- A company’s economic moat.
- Capital allocation.
To expand coverage, Morningstar also uses a statistical model to mimic how analysts make decisions. Equities analyzed by this tool have a “Q” superscript next to their respective rating.
What is a Morningstar 5-star rating? What is a Morningstar 4-star rating?
A 5-star stock is undervalued and trading at an attractive discount relative to its fair value estimate. A 4-star investment is moderately undervalued and trading at a slight discount.

Morningstar stock ratings
For illustrative purposes only.
Fair value estimate: is a stock a deal or overpriced?
The fair value estimate is an analyst’s projection of a stock’s true, long-term value. A stock earns a higher star rating if it’s trading below what Morningstar analysts think it’s worth. If a stock looks overpriced to analysts, it earns fewer stars.
With the Uncertainty Rating, Morningstar builds in a margin of safety. The more uncertain the estimate, the greater the discount investors want before buying. Uncertainty ratings range from low to extreme.
Analysts review factors like:
- Operating and financial leverage.
- Sales sensitivity to the overall economy.
- Product concentration.
- Pricing power.
- Exposure to material ESG risks.
- Company-specific factors.
Economic moats: holding off the competition
An economic moat measures a firm’s durable competitive advantage. If analysts expect a company will fend off competitors for 20 years, it receives a wide moat rating. A 10-year advantage earns a narrow moat. Firms with a short-lived or no competitive advantage get no moat.
Analysts must pitch wide-moat recommendations to an expert committee, composed of senior Morningstar equity researchers. They also award a positive, stable, or negative rating based on the trending direction of the moat.
Economic moats come from five sources:
- Switching costs—money, effort, or time—can dissuade customers from jumping to a competitor.
- The network effect is when a good or service becomes more valuable as more people use it.
- Intangible assets like patents, regulatory licenses, and brand identity can prevent competitors from copying products.
- A company with a cost advantage can produce goods or services at a lower cost, undercutting the competition or boosting profitability.
- Efficient scale benefits companies in a niche market that only supports a few competitors.
Assess capital allocation
The Capital Allocation Rating assesses where and how leadership uses excess profits. Do they return it to shareholders through dividends? Do they pay down their debt? Do they invest in product development?
Companies can receive a poor, standard, or exemplary rating.
History of Morningstar Ratings
Key Takeaways

The Morningstar Rating for funds, or the star rating, is an at-a-glance look at a fund’s risk-adjusted performance over the past three years.

The Morningstar Medalist Rating simplifies strategy selection for a broad universe of investments.

Morningstar Manager Research relies on three pillars: people, parent, and process.
Morningstar Ratings for Mutual Funds and ETFs
Morningstar ratings work together as a powerful tool to assess funds [PDF]. Morningstar covers over 294,000 open-end funds and 12,800 closed-end funds.
Morningstar began issuing star ratings for US-based exchange-traded funds in 2006. Analyst coverage debuted in 2008 as the investment vehicle gained traction in global markets. Morningstar ratings cover over 23,400 exchange-traded funds.

Morningstar mutual fund ratings
For illustrative purposes only.
The Morningstar rating for funds
Introduced in 1985, the Morningstar RatingTM for funds, often called the star rating, compares funds against their peers to inform investment decision-making. It’s an at-a-glance look at a fund’s risk-adjusted performance over the past three years.
The star rating shines a light on fees that can erode the ultimate returns on an investment. One trade-off: the rating only reflects historical returns, which don’t guarantee future performance.
The Morningstar Rating for funds follows a bell-curve distribution. The top 10% of funds in a category receive a 5-star rating. The next 22.5% receive a 4-star rating.
Estimate future performance with Morningstar Medalist Ratings
The Morningstar Medalist Rating simplifies how wealth and asset managers search for, select, and monitor investments. It offers one forward-looking assessment through a market cycle of at least five years.
The rating reflects an analyst’s conviction that a fund will outperform peers on a risk-adjusted basis. It includes three positive ratings—Gold, Silver, and Bronze.
- Gold-rated funds rank in the top 15% of their category with expected positive net-of-fee alpha.
- Silver-rated funds rank in the next 35% of products with expected positive alpha.
- Bronze funds in the bottom 50% of products that are predicted to have positive alpha.
- Neutral funds are expected to deliver zero or less than zero alpha.
- Negative funds, the worst designation, are ranked in the bottom 70% of the category’s products with subzero alpha.
The Medalist Rating combines humans and algorithms to expand Morningstar coverage. Algorithms replicate analyst findings using past rating decisions and the data behind them. The model continues to pick clearly over-and underperforming funds.
3 Pillars of Morningstar Manager Research
Morningstar’s more than 100 analysts operate globally with an added layer of local expertise. Independent research empowers asset and wealth managers with a forward-looking perspective on how investments might act in different market environments.
Researchers analyze Morningstar data and fund documents and, when possible, conduct face-to-face interviews with the fund management team.
The People pillar analyzes the person who manages a fund. Analysts look at factors like:
- Length of tenure.
- Qualified analysts.
- Relevant investment experience.
- Succession planning and team stability.
2. The Process pillar reflects how well managers execute their investment strategy over time. Analysts assess factors like:
- Investment philosophy behind a strategy.
- Investment research.
- Systematic and repeatable elements of a process.
- Approach to risk management.
- Manager decision-making.
- Loyalty to the strategy, especially when it’s out of favor.
3. The Parent pillar reviews the stewardship quality of a firm. Analysts look for qualities like:
- Recruitment and retention of talent.
- Quality of product lineup.
- Detailed preparation.
- Alignment of interests with investors.
- Regulatory compliance.
Morningstar ratings of other institutional investments
Morningstar’s growing coverage covers new forms of investments that are gaining popularity. World-class analysts take intentionally complicated offerings and break them down into fundamentals.
Separately managed accounts ratings
Since 2003, Morningstar has increased its coverage to 11,000 separately managed accounts. Recent technology advances have driven down account minimums, opening SMAs to a broader range of investors.
Forward-looking Medalist Ratings help investors compare options and tax-loss harvesting opportunities. SMAs can receive positive ratings of Gold, Silver, or Bronze, as well as neutral or negative ratings.
Morningstar also awards star ratings based on the risk-adjusted performance of an SMA over the trailing three years.
Collective investment trust ratings
Debuting in 2007, Morningstar CIT ratings cover 7,800 collective investment trusts. Retirement professionals can use the simplified rating system to compare investment vehicles.
The star rating reflects a CIT’s risk-adjusted performance over the past three years, compared to its peers. The Medalist Rating offers an analyst’s assessment of a trust’s ability to outperform others over time.
Morningstar ratings of 529 plans
A 529 education saving plan is an investment tool to pay for higher-education expenses. Morningstar ratings can help advisors compare tax-advantaged plans and recommend the best fit for parents.
Analysts award plans with Morningstar Medalist Ratings of Bronze, Silver, or Gold, with Gold-rated plans having the highest conviction.
Morningstar Model Portfolio Ratings
With model portfolios, advisors can dedicate more time to growing their business and less to investment management. Morningstar covers 4,600 model portfolios in its advanced tools for wealth and asset managers.
Powered by analyst assessment and machine learning, Morningstar awards model portfolios with Medalist Ratings of Bronze, Silver, or Gold. Gold-rated plans have the highest conviction. The star rating shows recent risk-adjusted performance.
Key Takeaways

Sustainability Ratings offer a measuring stick that slices through the confusion of conflicting, politicized terms.

The ESG Risk Assessment describes a company’s exposure to and management of material issues.

Carbon risk metrics indicate an investment’s exposure to future carbon-related risks such as regulation and price pressures.
Sustainability Ratings
As interest grows in sustainable investing, Morningstar ratings provide a clear, consistent look at risks and opportunities.
With sustainability ratings, advisors can show investors how the companies in their portfolios manage ESG risks compared to their peers. Advisory firms can build custom lists of suitable funds with a consistent standard.
Asset managers can use sustainability ratings to develop products and vet exclusions. It empowers firms to reach an emerging group of investors who want to incorporate ESG or sustainable-investing considerations into their investments.
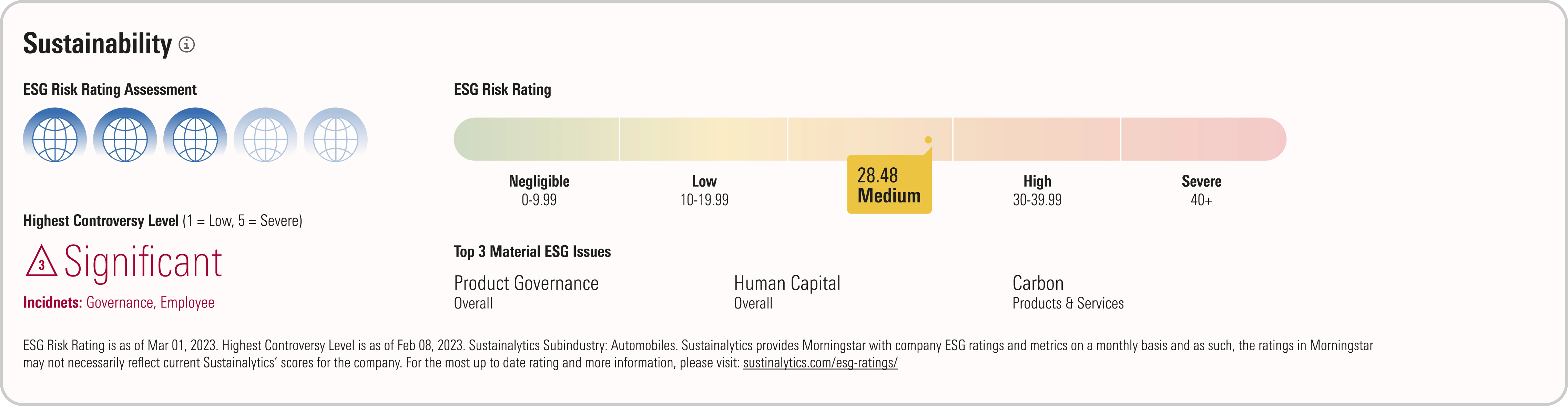
Morningstar ESG risk rating assessment
For illustrative purposes only.
Assessing ESG risk
Morningstar ratings visualize ESG risk in a consistent, common language.
The ESG Risk Assessment describes a company’s exposure to material ESG issues and how well they manage that risk. Unlike the star rating, the ESG Risk Assessment represents an absolute number you can compare across industries.
Morningstar Sustainalytics considers 20 material sustainability indicators that shape its total risk assessments. Reports also flag a company’s top three material ESG issues.
The Sustainability Rating for funds rolls up the ESG risks of underlying holdings. The 1-5 globe rating assesses how well companies in a portfolio manage ESG risk relative to their peers. A 1-globe rating represents high ESG risk; a 5-globe rating represents low ESG risk.
Controversy level
Corporate scandals can damage a firm’s reputation, trigger legal penalties, or inspire consumer boycotts. Controversies ratings can support investment decisions and help stakeholders manage reputational risks.
Sustainalytics assesses how controversies are likely to evolve over the next 12 to 24 months. Analysts monitor more than 700,000 daily news stories to flag ESG-related incidents. Our framework considers:
- Severity of incidents.
- Corporate accountability.
- If incidents form a pattern of corporate misconduct.

Carbon risk ratings
For illustrative purposes only.
Carbon Metrics
As global climate action ramps up, carbon risk metrics indicate an investment’s exposure to carbon related risks such as future regulation or price pressures.
The Morningstar® Portfolio Carbon Risk Score™ measures the risk that companies face from the transition to a low-carbon economy. For funds and portfolios, the score reflects the weighted average of the underlying holdings.
Morningstar® Portfolio Fossil Fuel Involvement™ assesses how exposed a company is to the fossil fuel industry, from extraction to distribution.
To earn the Morningstar® Low Carbon Designation™, companies need low carbon and fossil-fuel exposure.
What is the ESG Commitment Level?
The ESG Commitment Level assesses the ESG resources and expertise in a firm or strategy. It’s a way to gauge the truthfulness of sustainability marketing claims. The rating follows a four-point scale: Leader, Advanced, Basic, and Low.
The level offers a stamp of authenticity from an independent source that clients can trust.
To earn the leader designation, asset management firms must incorporate ESG principles into their investment programs to the greatest extent relative to peers. The assessment reviews a firm’s:
- Firm’s history of ESG investing.
- ESG policies.
- Company culture.
- Level and consistency of integrating ESG processes.
- Reporting on ESG metrics for its funds.
- Stewardship activities.
ESG Impact Metrics
As companies operate, their actions affect the world around them—these are known as externalities. These include greenhouse gas emissions, treatment of workers, community interactions, and more. Some investors want to understand what real-world outcomes result from their investments.
Impact metrics measure the environmental and social consequences of business activities, both positive and negative.
The Morningstar Sustainalytics ESG Impact Framework creates a common way to talk about issues that matter to investors. It offers consistent, meaningful assessments of company-level impact. Portfolio-level impact metrics can look across underlying holdings in a fund to assess the total footprint.
The ESG Impact Framework aligns with the internationally accepted UN Sustainable Development Goals. It simplifies the 17 SDGs into a handful of relevant themes:
- Basic Needs
- Human Development
- Climate Action
- Resource Security
- Healthy Ecosystems
Impact metrics fall into two buckets.
Operational metrics measure the impact of business activities. How much water does a company pull from its watershed? How often are workers injured on the job?
Sustainable activities metrics reflect the percentage of a company’s revenue that comes from business activities with a positive environmental or social impact. A car manufacturer could mitigate climate change by producing electric vehicles, or a pharmaceutical company could research cures for neglected diseases.
Credit Ratings
Credit ratings measure a borrower’s capacity to repay a debt. With thorough due diligence, analysts assess the likelihood of company, entity, or government defaulting on a loan. Credit ratings can affect the interest rates an entity must pay on a loan.
DBRS Morningstar rates more than 5,000 credit issuers and 60,000 securities worldwide.
Credit ratings range from AAA (low credit risk) to a C (increased credit risk). At each level except the highest, AAA, (high) represents the top performers and (low) the bottom. DBRS credit ratings help investors compare types of debt across asset classes.
Researchers specialize in four main sectors, each with their own methodology:
- Corporate finance.
- Financial institutions.
- Governments.
- Structured finance.
Retired Morningstar Ratings
As Morningstar responds to an evolving market, our research team revisits and improves our research methods. Below are some of our retired rating systems.
The Morningstar Quantitative Rating and the Morningstar Analyst Rating
The advent of the Morningstar Medalist Rating marks the sunsetting of the Morningstar Quantitative Rating (Notated with Q) and the Morningstar Analyst Rating.
Analysts remain the cornerstone of the Morningstar process.
Machine learning extends analyst views to a wider investment universe with inheritance logic. This means that funds can inherit ratings from other funds with related analyst decisions. For example, the People analyst rating would apply to all funds managed by the same team.
Quantitative ratings inherit half (55%) of their pillar ratings directly from analysts.
Our researchers will continue to rate and review funds. For transparency, new data points will show the percentage breakdown of analyst and algorithmic input in assigning a rating.
Five Pillars of Morningstar Research
Morningstar believes that a meaningful fund performance assessment happens in the context of broader evaluation. Analysts not only analyze each pillar—which formerly included parent, process, people, performance, and price—but the interaction between them.
Analysts decided to eliminate the separate performance and price pillars, incorporating both into the remaining pillars.
The Stewardship Rating
In 2020, Morningstar renamed the stewardship rating to the Morningstar Capital Allocation Rating to prevent confusion with ESG ratings.
Investment Research is issued and produced by subsidiaries of Morningstar, Inc.’s Research Group which consists of various wholly owned subsidiaries of Morningstar, Inc. including, but not limited to, Morningstar Research Services LLC. Morningstar Research Services LLC is registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission.
