Introducing the Morningstar Sustainability Rating for Funds
Our new Sustainability Rating provides a reliable, objective way to evaluate how investments are meeting environment, social, and governance challenges.
Sustainability is a big deal to a lot of people today. In survey after survey, citizens express concern about climate change, environmental issues, the ways companies treat their workers, and corporate social responsibility.
But it can be hard for investors who care about these issues to put their money where their values are.
Only a small subset of funds (around 2% globally) have explicit mandates to care about these issues. When you weed out those that have haven't established strong performance records or don't otherwise meet your investment goals, there just aren't that many options. For many investors using retirement accounts like 401(k)s, there may be no options at all. And even if you found a sustainable-focused fund, there has been no easy way to evaluate independently how well these funds are actually living up to their sustainability promises.
The new Morningstar Sustainability Rating helps investors address those challenges and put sustainable investing into practice. In a nutshell, the rating evaluates funds based on the sustainability profile of their underlying holdings and is applied to all funds for which we have sufficient data not just those that have an explicit mandate to focus on sustainability. This means investors who care about sustainability can now can explore a much broader universe of funds (20,000 globally) when building and evaluating their portfolios.
Our Sustainability Rating is not the last word on sustainability, but an important first step toward providing investors with better tools to evaluate and compare funds based on sustainable investing principles. The rating helps investors answer fundamental questions such as, how well are the companies that my fund owns managing the risks and opportunities associated with the sustainability challenges they face? And the rating does so objectively and robustly, leveraging fund holdings data, calculating portfolio scores, and comparing funds in a uniform, reliable way.
What Is Sustainability? Many investors are familiar with the term socially responsible investing (SRI), which is still used today and often shortened to just "responsible investing." SRI is a values-based investment process that primarily uses exclusionary screening to weed out exposure to certain types of products or industries (such as tobacco or gambling) coupled with active ownership (proxy voting, filing or cosponsoring shareholder resolutions, and direct company engagement).
Over time, though, many SRI-oriented investors started getting more interested in issues such as the environment, workplace policies, product safety, and the global supply chain. Investors couldn't simply exclude these concerns from a portfolio without more extensive evaluation and analysis. These topics broadly became known as environmental, social, and governance, or ESG, issues.
Responsible investing evolved to include ESG, which led to the development of ESG analysis of companies. As a result, research firms such as Sustainalytics--whose company-level ESG data underpins Morningstar's Sustainability Ratings--play an important role in analyzing companies across a wide spectrum of ESG issues. Increasingly, corporate issuers are providing sustainability reporting, making it easier for research firms and investors to evaluate the ESG-related risks and opportunities associated with an investment in a company.
Today, terms like "responsible investing," "sustainable investing," and "ESG" are used in similar or even interchangeable fashion. An even newer term is "impact investing," which refers to attempts to measure the positive environmental or social outcomes of a given investment.
At Morningstar, we prefer the term "sustainable investing" to best capture the essence of both its values-based orientation, as well as the view that it just makes sense to include ESG in a thorough investment analysis.
How the Rating Works The Morningstar Sustainability Rating is a measure of how well the companies held by a fund are managing their ESG risks and opportunities when compared with similar funds. We use company-level ESG data from Sustainalytics, a leading provider of ESG ratings and research, to calculate the rating.1 All funds with at least 50% of their assets in firms that have been assigned company-level ESG ratings by Sustainalytics will receive a rating.
A Two-Step Process

We assign a fund's Sustainability Rating in two steps: First, we derive a Morningstar Portfolio Sustainability Score. This score is an asset-weighted average of a portfolio's normalized company-level ESG scores with deductions made for any controversies surrounding the companies owned 'by the fund. (For further information on Sustainalytics' scoring methodology, refer to the Morningstar Sustainability Rating methodology document. We normalize Sustainalytics' company ESG scores to make them comparable across industry peer groups, which is necessary when scoring diversified portfolios.
Next, we sort funds into five normally distributed groups by comparing a fund's Portfolio Sustainability Score with that of its Morningstar Category peers.
Morningstar Sustainability Rating
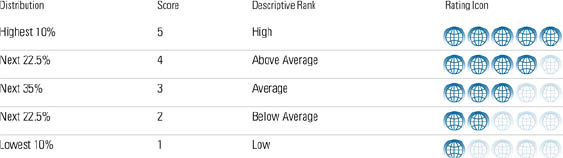
Using the Sustainability Rating Investors, and those helping them make decisions, can use the Portfolio Sustainability Score to evaluate how well the companies in a portfolio are managing their ESG risks and opportunities relative to their industry peer groups. Scores above 50 indicate that, on average, a fund's holdings place in the top half of their industry peer groups.2 Investors can use the Sustainability Rating to evaluate a fund relative to other funds in the same Morningstar Category.
Fund Rating Example
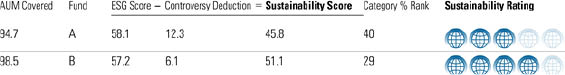
Investors can use the rating to evaluate how well the funds they already hold are applying best sustainable investing practices or to evaluate prospective investments through an ESG lens. They can also use the rating to assess how well SRI funds are living up to their mandates. Finally, the rating and supporting analytics afford investors a wealth of data that they can sift through in drawing their own conclusions about the investing payoff--in financial risk and reward terms--of incorporating sustainable principles into a portfolio.3
Learn more and see our full coverage of the the Morningstar Sustainability Rating.
1 We use two main elements of Sustainalytics research: Company ESG Ratings and Controversy assessments. Sustainalytics covers more than 4,500 companies globally, assigning ESG Ratings based on annual company evaluations relative to their global industry peer groups. Sustainalytics' analysts use a peer-group-specific mix of key indicators in each of the three broad areas (environmental, social, and governance) to capture the most relevant ESG issues in each peer group. The resulting Company ESG Rating comprises a score and peer group ranking, as well as underlying scores and rankings for each of the three--E, S, and G--components. Controversy assessments are incidents that companies are involved in related to ESG issues, which Sustainalytics identifies and monitors in real time. The firm covers more than 10,000 companies with Controversy assessments. Controversies are grouped based on severity from Category 1 (Low) to Category 5 (High), along with an outlook assessment on whether the situation is trending worse or improving. Sustainalytics likens the severity scale to a hurricane warning system, meaning that the degree of seriousness rises exponentially from lower to higher categories.
2 As a portfolio-based metric, the Sustainability Rating does not reflect exclusionary screening. In other words, funds aren't automatically rewarded or penalized for excluding certain companies or industries. Neither does the rating reflect the active ownership activities, including company engagement, of many SRI funds. The rating measures how well the companies in a portfolio are managing their ESG risks and opportunities relative to their industry group peers.
3 The Sustainability Rating is portfolio-based, not performance-based. It should be used alongside traditional risk, return, and style metrics as well as qualitative assessments of a fund's investment process and how well it has been executed over time. As a purely portfolio-based measure, the Sustainability Rating has no impact on the Morningstar Rating for funds, or vice versa. The same goes for the Stewardship Grades we give to asset managers. While it doesn't automatically have an impact on our Analyst Rating for funds, it is an additional metric our analysts can consider alongside many others in their evaluations.
Jon Hale has been researching the fund industry since 1995. He is Morningstar’s director of ESG research for the Americas and a member of Morningstar's investment research department. While Morningstar typically agrees with the views Jon expresses on ESG matters, they represent his own views.

/s3.amazonaws.com/arc-authors/morningstar/42c1ea94-d6c0-4bf1-a767-7f56026627df.jpg)
:quality(80)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/morningstar/OMVK3XQEVFDRHGPHSQPIBDENQE.jpg)
:quality(80)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/morningstar/WJS7WXEWB5GVXMAD4CEAM5FE4A.png)